File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is the commonly used protocol for exchanging files over the Internet. FTP uses the Internet’s TCP/IP protocols to enable data transfer. FTP uses a client-server architecture, often secured with SSL/TLS. FTP promotes sharing of files via remote computers with reliable and efficient data transfer.
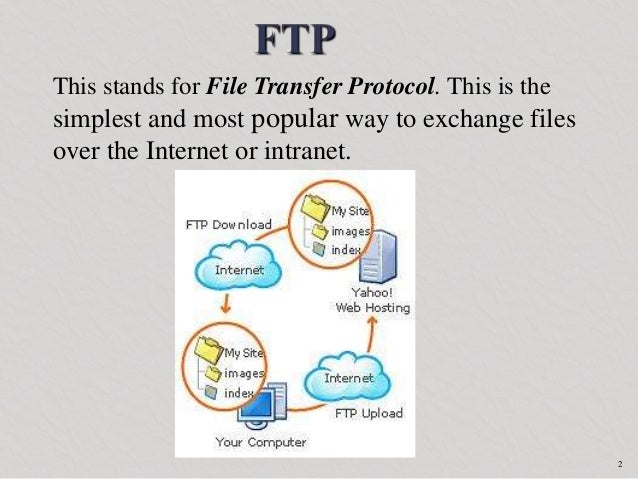
How FTP Works
FTP works in the same way as HTTP for transferring Web pages from a server to a user’s browser and SMTP for transferring electronic mail across the Internet in that, like these technologies.
FTP uses a client-server architecture. Users provide authentication using a sign-in protocol, usually a username and password, however some FTP servers may be configured to accept anonymous FTP logins where you don’t need to identify yourself before accessing files. Most often, FTP is secured with SSL/TLS.
How to FTP
Files can be transferred between two computers using FTP software. The user’s computer is called the local host machine and is connected to the Internet. The second machine, called the remote host, is also running FTP software and connected to the Internet.
- The local host machine connects to the remote host’s IP address.
- The user would enter a username/password (or use anonymous).
- FTP software may have a GUI, allowing users to drag and drop files between the remote and local host. If not, a series of FTP commands are used to log in to the remote host and transfer files between the machines.
Common Uses of FTP
FTP is most commonly used to download a file from a server using the Internet or to upload a file to a server (e.g., uploading a web page file to a Web server).